9- Threatened and endangered species (plants and animals)
Haiti is considered as one of the most biologically country of the West Indies. Haiti has 5600 species of plant; however, 36 % are considered endemic of the island. Less than 5 % of Haiti's land is officially accounted for public land and the remaining are private land. Because of the scarcity of electricity, poverty and unemployment, a large part of the population has been used wood as cooking fuel which causes the forest has been depleted. On the other hand, many species of plants and animals have become extinct because our forests are almost gone.a- Threatened species of mammals
Endangered mammals in the country such as:1- the Haitian solenodon (Solenodon paradoxus)
2- the Hispaniolan hutia (Plagiodontia aedium).
3- A number of species of rodents formerly present have been driven to extinction, including
montane hutia (Isolobodon montanus),
4- Puerto Rican hutia (Isolobodon portoricensis),
5- Samana hutia (Plagiodontia ipnaeum),
6- twisted-toothed mouse (Quemisia gravis),
7- Lemke’s hutia(Rhizoplagiodontia lemkei),
8- Hispaniolan edible rat (Brotomys voratus) and
9- Imposter hutia (Hexolobodon phenax).
a- Haiti: Saving the Environment, Preventing Instability and Conflict was published Latin America and Caribbean Briefing N°20 in Port-au-Prince/Brussels, 28 April 2009. International Crisis Group which is works to prevent conflict worldwide. This article presents an overview of the causes of environmental issues in Haiti. This article presents the historical background of environmental crisis in Haiti which includes facts and data. Further, it highlights the state weakness and lack of environmental policies, extreme poverty, rapid population growth and urban overcrowding as the most significant causes of environmental issues that required an immediate answer before this problem reach its climax. [Click here to read the full article]
b- Centre Internatioal de Hautes Etudes Agronomiques Mediterraneene, Zaragoza (Spain) publish an article that describe how the increasing of the Haitian population causes the problem of environmental degradation to get worse day by day. Due to the fact that many farmers have left the country dramatically to move to the urban area in order to get a job which has complicated the problem. There is no enough infrastructure in the cities for this high density and that uncontrolled population which seriously endanger the maintenance of environmental balance. [Click here to read the full article]
c- Impact socioéconomique de la dégradation des terres en Haïti et interventions pour la réhabilitation du milieu cultivé is an article published by Alex Bellande where he highlighted the roots of the phenomenon of deforestation in Haiti which results particularly the acceleration of timber for charcoal production and commercial logging during the second half of the 19th century. It emphasize an important fact that I had not heard about it before where he mentioned that wood often occupy the second place in the foreign trade during the 19th and 20th centuries. [Click here to read the full article]
b- Foxx Richard M. “The Earth is Tired: Reversing deforestation in Haiti”. Willey Online Library. Published April 1, 2012. [Accessed: March 18, 2014]. Available online: [Click here to read the full magazine].
c- Amiel Blajchman . “Haiti’s Poverty is Directly Linked to Deforestation and Habitat Loss”. RED* BLUE & GREEN. Published on May 10th, 2009. [ Accessed : March 18, 2014]. Available online: [Click here to read the full magazine]
4- Puerto Rican hutia (Isolobodon portoricensis),
5- Samana hutia (Plagiodontia ipnaeum),
6- twisted-toothed mouse (Quemisia gravis),
7- Lemke’s hutia(Rhizoplagiodontia lemkei),
8- Hispaniolan edible rat (Brotomys voratus) and
9- Imposter hutia (Hexolobodon phenax).
B- Endangered species of birds
Two species of birds are considered as threatened species in Haiti :
1- Hispaniolan Trogon (Priotelus roseigaster),
2- Grey-crowned Palm-tanager (Phaenicophilus poliocephalus).
1- Hispaniolan ventriloquial frog,
2- Macaya breast-spot frog,
3- La Hotte glanded frog,
4- Macaya burrowing frog,
5- Mozart's frog and
6- Hispaniolan crowned frog.
C- Endangered species of amphibians
Six species of frogs have been considered as extinct species:1- Hispaniolan ventriloquial frog,
2- Macaya breast-spot frog,
3- La Hotte glanded frog,
4- Macaya burrowing frog,
5- Mozart's frog and
6- Hispaniolan crowned frog.
References
1- World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1992). Nearctic and Neotropical. IUCN. pp. 384–. ISBN 978-2-8317-0093-9 [Internet]. [Cited March 1, 2014]. Available from:
2- Hispaniola Solenodon , 2013 . Endangered animals in Haiti
[Internet]. List of Countries of the World.com [Cited March 1, 2014]. Available
from: http://thewebsiteofeverything.com/animals/
3- Animals in Haiti, 2013 . Endangered animals in Haiti [Internet]. List of Countries of the World.com [Cited March 1, 2014]. Available from: http://www.listofcountriesoftheworld.com/ha-animals.html
4- Bryan Walsh, 2011. Amid the Ruins of Haiti, Conservationists
Find Endangered Frogs [Internet]. Time, Science and Space. [Cited March 1, 2014].
Available from: http://science.time.com/2011/01/11/wildlife-amid-the-ruins-of-haiti-conservationists-find-endangered-frogs/
10- Three Popular articles about the ecosystems or environment in Haiti.
b- Centre Internatioal de Hautes Etudes Agronomiques Mediterraneene, Zaragoza (Spain) publish an article that describe how the increasing of the Haitian population causes the problem of environmental degradation to get worse day by day. Due to the fact that many farmers have left the country dramatically to move to the urban area in order to get a job which has complicated the problem. There is no enough infrastructure in the cities for this high density and that uncontrolled population which seriously endanger the maintenance of environmental balance. [Click here to read the full article]
c- Impact socioéconomique de la dégradation des terres en Haïti et interventions pour la réhabilitation du milieu cultivé is an article published by Alex Bellande where he highlighted the roots of the phenomenon of deforestation in Haiti which results particularly the acceleration of timber for charcoal production and commercial logging during the second half of the 19th century. It emphasize an important fact that I had not heard about it before where he mentioned that wood often occupy the second place in the foreign trade during the 19th and 20th centuries. [Click here to read the full article]
11- Three Peer- reviewed articles about the management of the ecosystems in Haiti.
a- Dr. Vereda Johnson Williams, 2011. A Case Study of Desertification in Haiti[Internet]. Journal of Sustainable Development. Available from: [Click here to read the full magazine]
b- Haiti-Environment: from the « Pearl of the Antilles » to desolation is a peer-reviewed written by a famous Haitian journalist after a devastated tropical storm brought the live of 3,000 people, most drowning in the city of Gonaives, Haiti. This event happened in 2004 and cause million of dollars for the reparation. The reason that caused this disaster is that this city is located in above the sea level; however, this city is surrounding the high ranges of mountains which become open area because of deforestation. [Click here to read the full peer-reviewed articles]
c- Pellek R.1997. Combating Tropical Deforestation in Haiti. [Internet]. Cab Direct. Available from: [Click here to access the abstract]
c- Pellek R.1997. Combating Tropical Deforestation in Haiti. [Internet]. Cab Direct. Available from: [Click here to access the abstract]
13- Three articles the animals and plants
a- New Wildlife Reserve in Haiti to Protect Critically Endangered Iguana Species was posted on June 2013 in Eco-Exchange by by Dipika Chawla, Rainforest Alliance. The purpose of this articles is to introduce am entirely subpopulation of iguana known as Ricord’s iguanas discovered in 2007 by the biologist Ernst Rupp in a Haitian Town Anse-a-Pitres. This population of iguana is extremely fragile because of deforestation and drought. Grupo Jaragua which partnership with International Iguana Foundation (IIF) is working which a youth local organization in order to advocate for conservation of the area as well to monitor this iguana species of extinction. [Click here to read the full Peer-Reviewed article
b- Foxx Richard M. “The Earth is Tired: Reversing deforestation in Haiti”. Willey Online Library. Published April 1, 2012. [Accessed: March 18, 2014]. Available online: [Click here to read the full magazine].
c- Amiel Blajchman . “Haiti’s Poverty is Directly Linked to Deforestation and Habitat Loss”. RED* BLUE & GREEN. Published on May 10th, 2009. [ Accessed : March 18, 2014]. Available online: [Click here to read the full magazine]

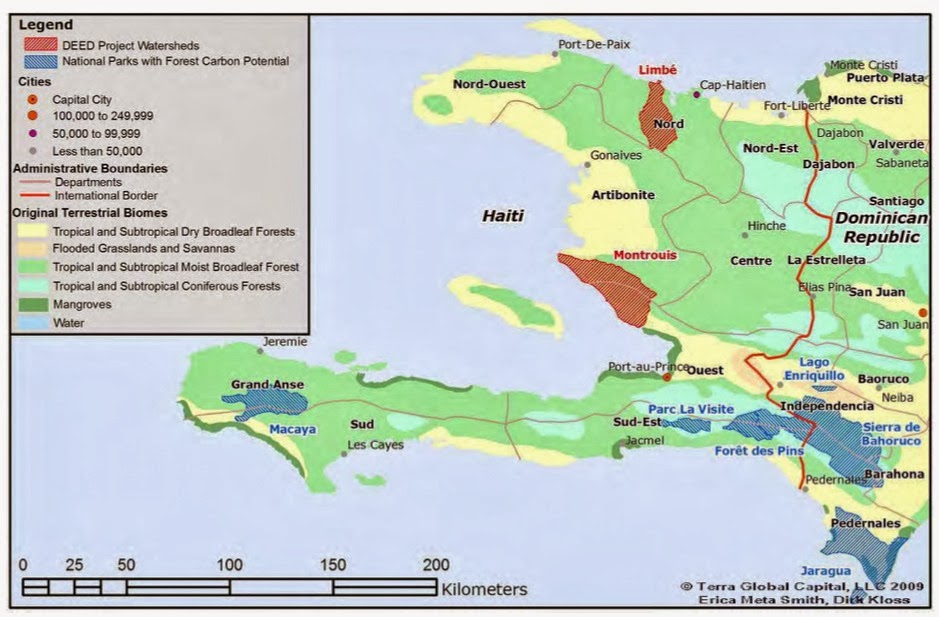

.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)